Unveiling the intricate world of molecular compounds, this comprehensive guide, worksheet molecular compounds answer key, serves as a beacon of knowledge, illuminating the fundamental principles that govern their formation, nomenclature, properties, and ubiquitous presence in our daily lives. Delve into the fascinating realm of covalent bonding and discover the secrets that unlock the mysteries of these essential chemical entities.
Worksheet molecular compounds answer key delves into the intricacies of molecular compounds, providing a roadmap for understanding their unique characteristics and behavior. This guide unravels the IUPAC rules that govern their nomenclature, empowering readers to decipher the language of chemistry.
By exploring their physical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, and solubility, we gain insights into the interplay between structure and bonding.
Molecular Compounds: Worksheet Molecular Compounds Answer Key

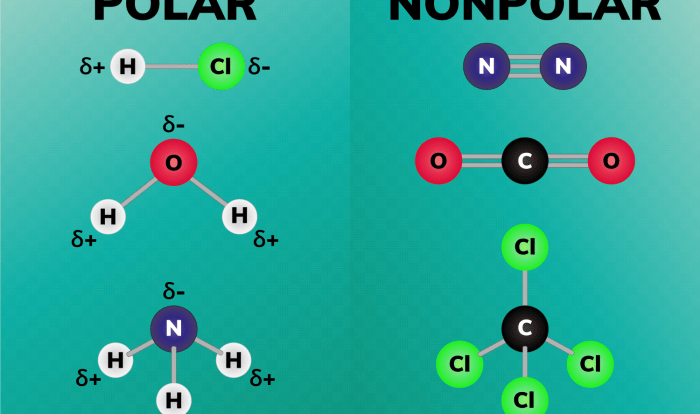
Molecular compounds are chemical compounds that are formed by the covalent bonding of atoms. They are typically composed of two or more non-metallic elements, and their properties differ significantly from those of ionic compounds.
Unlike ionic compounds, which are held together by electrostatic forces between positively and negatively charged ions, molecular compounds are held together by the sharing of electrons between atoms. This sharing of electrons creates covalent bonds, which are stronger than the electrostatic forces in ionic compounds.
Nomenclature of Molecular Compounds
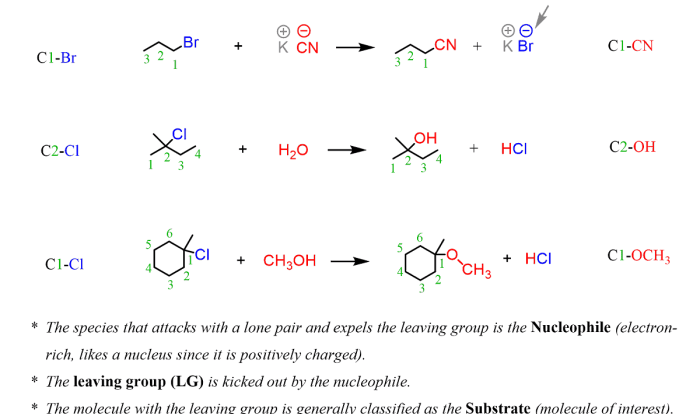
The IUPAC rules for naming molecular compounds are based on the number and type of atoms present in the molecule. For binary molecular compounds, which contain only two elements, the first element is named using the root of its element name, and the second element is named using the suffix -ide.
Prefixes are used to indicate the number of atoms of each element in the molecule.
- For example, the compound CO2 is named carbon dioxide, indicating that it contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
- The compound NH3 is named ammonia, indicating that it contains one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms.
Properties of Molecular Compounds
The physical properties of molecular compounds are largely determined by their structure and bonding. Molecular compounds typically have lower melting points and boiling points than ionic compounds because the covalent bonds between the atoms are weaker than the electrostatic forces in ionic compounds.
Molecular compounds are also generally less soluble in water than ionic compounds because they do not form ions in solution. However, some molecular compounds, such as alcohols and sugars, are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Molecular Compounds in Everyday Life, Worksheet molecular compounds answer key
Molecular compounds are found in a wide variety of everyday products, including plastics, fuels, and pharmaceuticals. Plastics are made from polymers, which are long chains of repeating molecular units. Fuels, such as gasoline and natural gas, are composed of hydrocarbons, which are molecular compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms.
Pharmaceuticals are often molecular compounds that have been designed to interact with specific biological targets in the body. For example, the drug aspirin is a molecular compound that is used to relieve pain and inflammation.
Key Questions Answered
What are molecular compounds?
Molecular compounds are chemical compounds composed of two or more non-metal elements that are covalently bonded.
How do molecular compounds differ from ionic compounds?
Molecular compounds are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms, while ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
What is the role of covalent bonds in molecular compounds?
Covalent bonds are the chemical bonds that hold the atoms of a molecular compound together.