Review sheet exercise 15 spinal cord and spinal nerves – Embark on a captivating journey with Review Sheet Exercise 15, where we unravel the intricacies of the spinal cord and spinal nerves. This exercise delves into the structure, functions, and clinical significance of these vital components, providing a comprehensive understanding of their roles in human anatomy and physiology.
The spinal cord, a crucial pathway for communication between the brain and the rest of the body, serves as the centerpiece of this exploration. We will uncover its organization and functions, unraveling its role in motor control, sensory perception, and reflex actions.
Additionally, we will delve into the clinical significance of spinal cord injuries and disorders, highlighting their impact on human health and well-being.
Spinal Cord
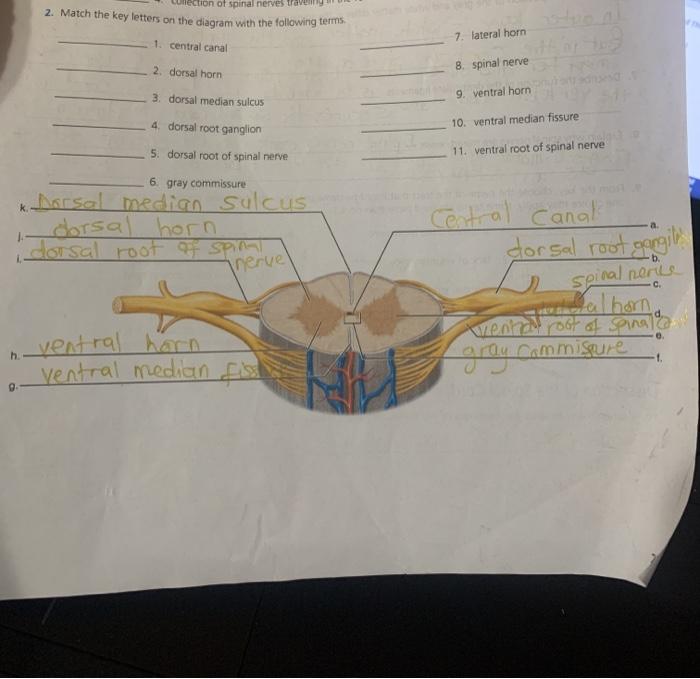
The spinal cord is a long, cylindrical bundle of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem to the lower back. It is responsible for transmitting sensory and motor signals between the brain and the rest of the body. The spinal cord is also involved in a number of reflex actions, such as the knee-jerk reflex.
Structure and Organization of the Spinal Cord
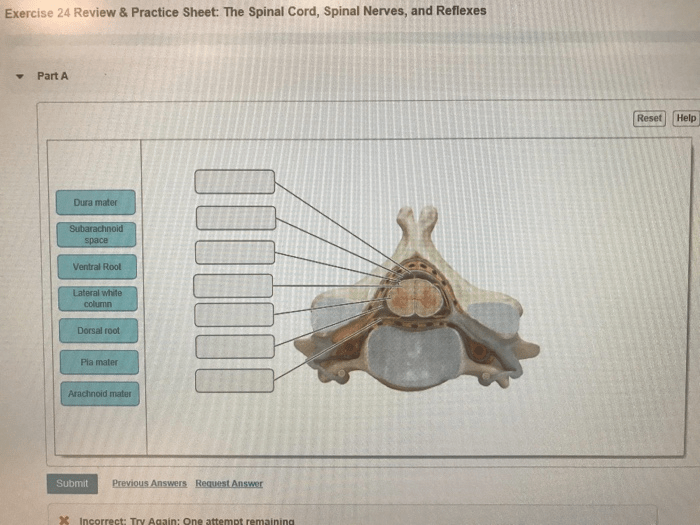
The spinal cord is divided into 31 segments, each of which gives rise to a pair of spinal nerves. The spinal cord is surrounded by three layers of meninges, which are tough, protective membranes. The outermost layer is the dura mater, which is followed by the arachnoid mater and the pia mater.
The spinal cord is also divided into gray matter and white matter. The gray matter is located in the center of the spinal cord and contains the cell bodies of neurons. The white matter is located on the outside of the spinal cord and contains the axons of neurons.
Functions of the Spinal Cord
The spinal cord has a number of important functions, including:
- Transmitting sensory and motor signals between the brain and the rest of the body
- Controlling reflex actions
- Regulating blood pressure and body temperature
Clinical Significance of the Spinal Cord, Review sheet exercise 15 spinal cord and spinal nerves
Damage to the spinal cord can have a devastating impact on a person’s life. Spinal cord injuries can result in paralysis, loss of sensation, and incontinence. There is no cure for spinal cord injuries, but there are treatments that can help to improve function and quality of life.
Spinal Nerves
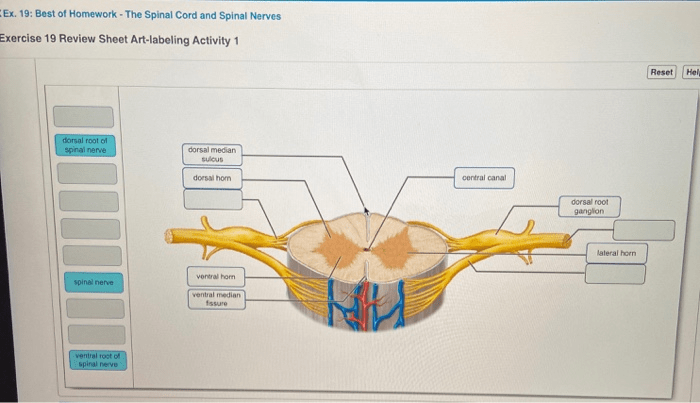
Spinal nerves are the nerves that branch off from the spinal cord. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, each of which corresponds to a segment of the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are responsible for transmitting sensory and motor signals between the spinal cord and the rest of the body.
Structure and Organization of Spinal Nerves
Each spinal nerve is composed of a dorsal root and a ventral root. The dorsal root contains sensory neurons, which transmit sensory signals from the body to the spinal cord. The ventral root contains motor neurons, which transmit motor signals from the spinal cord to the muscles.
Functions of Spinal Nerves
Spinal nerves have a number of important functions, including:
- Transmitting sensory and motor signals between the spinal cord and the rest of the body
- Controlling reflex actions
- Regulating blood pressure and body temperature
Clinical Significance of Spinal Nerves
Damage to spinal nerves can have a variety of symptoms, depending on which nerve is affected. Symptoms can include pain, numbness, weakness, and paralysis. Treatment for spinal nerve damage depends on the cause of the damage.
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Interactions: Review Sheet Exercise 15 Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves
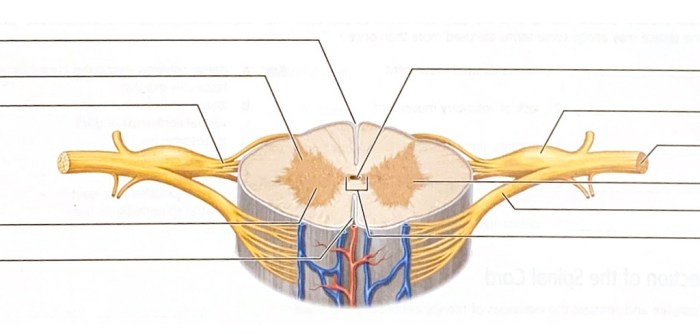
The spinal cord and spinal nerves interact in a number of ways. The spinal cord sends signals to the spinal nerves, which then transmit those signals to the rest of the body. The spinal nerves also send signals back to the spinal cord, which then transmits those signals to the brain.
This two-way communication is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system.
Clinical Significance of the Interaction Between the Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
Damage to the spinal cord or spinal nerves can disrupt the communication between the brain and the rest of the body. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, including pain, numbness, weakness, and paralysis. Treatment for damage to the spinal cord or spinal nerves depends on the cause of the damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of the spinal cord?
The spinal cord serves as the primary conduit for communication between the brain and the rest of the body, facilitating the transmission of motor commands and sensory information.
How do spinal nerves contribute to sensory perception?
Spinal nerves carry sensory information from the body to the spinal cord and brain, enabling us to perceive touch, temperature, pain, and other sensations.
What are some common clinical implications of spinal cord injuries?
Spinal cord injuries can result in a range of impairments, including paralysis, sensory loss, and autonomic dysfunction, depending on the severity and location of the injury.