Healthstream restraint and seclusion answers provide a comprehensive overview of the ethical, legal, and practical considerations involved in using restraint and seclusion in healthcare settings. This guide explores the different types of restraint and seclusion, the indications for their use, and the procedures for implementing and monitoring them.
Understanding the complexities of healthstream restraint and seclusion is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure patient safety and well-being while respecting their rights and dignity.
1. Healthstream Restraint and Seclusion Overview
Healthstream restraint and seclusion refer to the use of physical or mechanical measures to restrict a patient’s freedom of movement or to isolate them from others.
The purpose of healthstream restraint and seclusion is to protect the patient, staff, and others from harm, and to provide a safe environment for treatment. The goals of healthstream restraint and seclusion include:
- Preventing the patient from harming themselves or others
- Maintaining a safe environment for treatment
- Reducing the risk of elopement
There are ethical considerations related to healthstream restraint and seclusion, including:
- The patient’s right to autonomy
- The potential for abuse
- The need to use the least restrictive measures possible
2. Types of Healthstream Restraint and Seclusion
Types of Healthstream Restraint, Healthstream restraint and seclusion answers
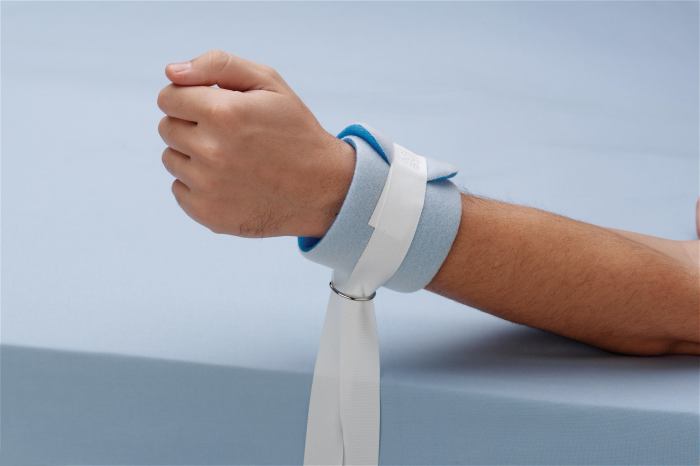
- Physical restraint: Involves the use of physical force or devices to restrict a patient’s movement.
- Mechanical restraint: Involves the use of mechanical devices, such as straps or cuffs, to restrict a patient’s movement.
Types of Healthstream Seclusion
- Isolation: Involves separating a patient from others for a period of time.
- Seclusion: Involves confining a patient to a locked room for a period of time.
Each type of restraint or seclusion may be used in different situations, depending on the patient’s needs and the clinical situation.
3. Indications for Healthstream Restraint and Seclusion
Indications for Healthstream Restraint
- When the patient is at imminent risk of harming themselves or others
- When the patient is unable to control their behavior and poses a danger to themselves or others
- When the patient is elopement risk
Indications for Healthstream Seclusion
- When the patient is at risk of harming themselves or others and cannot be safely managed in a less restrictive setting
- When the patient’s behavior is disruptive and cannot be managed in a less restrictive setting
- When the patient needs to be isolated for medical reasons, such as infection control
It is important to note that healthstream restraint and seclusion should only be used as a last resort, after all other less restrictive measures have failed.
4. Procedures for Healthstream Restraint and Seclusion
Steps Involved in Implementing Healthstream Restraint
- Obtain a physician’s order for restraint.
- Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain their consent, if possible.
- Use the least restrictive restraint possible.
- Monitor the patient closely while in restraint.
- Document the use of restraint, including the reason for restraint, the type of restraint used, and the patient’s response.
Steps Involved in Implementing Healthstream Seclusion
- Obtain a physician’s order for seclusion.
- Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain their consent, if possible.
- Use the least restrictive seclusion possible.
- Monitor the patient closely while in seclusion.
- Document the use of seclusion, including the reason for seclusion, the type of seclusion used, and the patient’s response.
5. Monitoring and Documentation for Healthstream Restraint and Seclusion

It is important to monitor patients in restraint or seclusion closely to ensure their safety and well-being.
The documentation required for healthstream restraint and seclusion includes:
- The reason for restraint or seclusion
- The type of restraint or seclusion used
- The patient’s response to restraint or seclusion
- The duration of restraint or seclusion
- Any injuries or adverse events that occur
Examples of monitoring and documentation tools include:
- Observation charts
- Incident reports
- Progress notes
6. Training and Education for Healthstream Restraint and Seclusion: Healthstream Restraint And Seclusion Answers

Staff who use healthstream restraint and seclusion must be properly trained and educated.
Training requirements include:
- The indications for restraint and seclusion
- The procedures for implementing restraint and seclusion
- The monitoring and documentation requirements
Education requirements include:
- The ethical considerations related to restraint and seclusion
- The legal and regulatory considerations related to restraint and seclusion
- The use of de-escalation techniques
Examples of training and education programs include:
- In-service training
- Online training
- Continuing education courses
7. Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Healthstream Restraint and Seclusion
There are legal and regulatory considerations related to healthstream restraint and seclusion.
The patient’s rights related to restraint and seclusion include:
- The right to be free from unnecessary restraint or seclusion
- The right to be informed about the reasons for restraint or seclusion
- The right to have a review of the restraint or seclusion order
Examples of legal cases or regulations related to healthstream restraint and seclusion include:
- The Joint Commission’s standards for restraint and seclusion
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ regulations for restraint and seclusion
- State laws and regulations governing restraint and seclusion
Top FAQs
What is the purpose of healthstream restraint and seclusion?
Healthstream restraint and seclusion aim to protect patients and staff from harm when a patient’s behavior poses a risk to themselves or others.
What are the different types of healthstream restraint?
Types of healthstream restraint include physical restraint, chemical restraint, and environmental restraint.
What are the indications for using healthstream restraint?
Restraint may be used when a patient is at imminent risk of harming themselves or others, or when they are unable to care for their basic needs due to a psychiatric or medical condition.