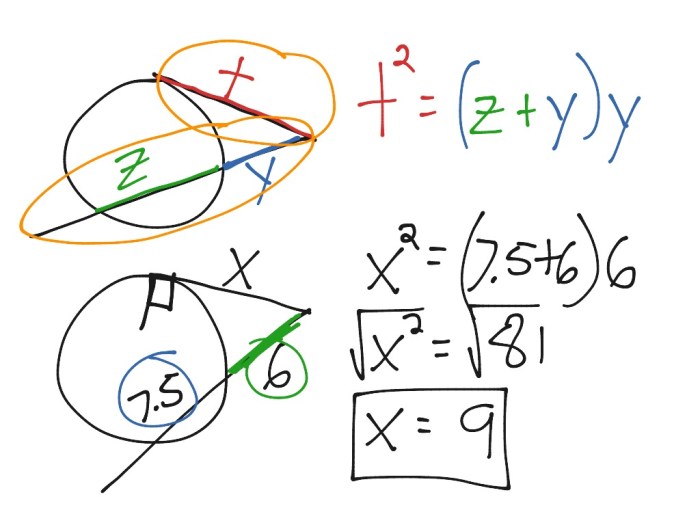Practice 12 4 angle measures and segment lengths answer key – Delving into the intricacies of angle measures and segment lengths, Practice 12.4 provides a comprehensive exploration of these fundamental concepts, unraveling their relationships and practical applications. This answer key serves as an invaluable resource, guiding students through the intricacies of angle and segment length relationships, empowering them to solve complex problems with confidence.
Through a series of carefully crafted problems, this answer key reinforces the understanding of angle measure relationships, including complementary, supplementary, and vertical angles. It further delves into segment length relationships, examining congruent, parallel, and perpendicular segments. Each problem is meticulously explained, providing step-by-step solutions that illuminate the underlying principles.
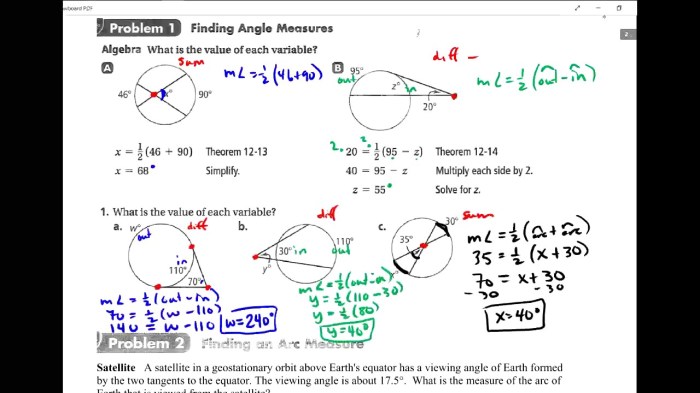
Angle Measure Relationships: Practice 12 4 Angle Measures And Segment Lengths Answer Key
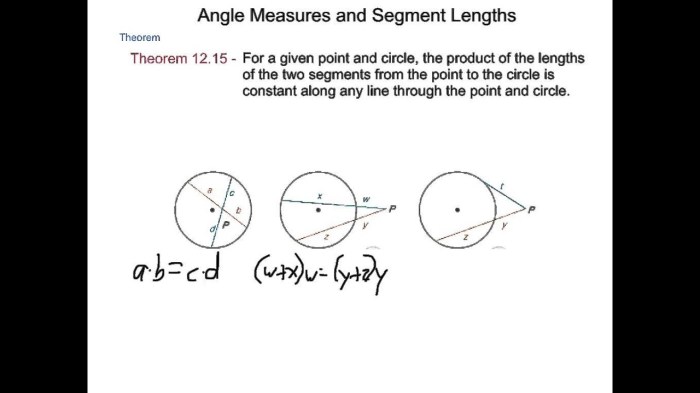
In geometry, the relationships between angles formed by intersecting lines play a crucial role in understanding and solving problems. These relationships help determine the measures of angles based on their positions and orientations.
There are three main types of angle relationships:
Complementary Angles, Practice 12 4 angle measures and segment lengths answer key
Complementary angles are two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees. When two lines intersect, they form four angles. If two of these angles are complementary, then the other two are also complementary.
Supplementary Angles
Supplementary angles are two angles whose measures add up to 180 degrees. When two lines intersect, they form two pairs of supplementary angles. Each pair of opposite angles is supplementary.
Vertical Angles
Vertical angles are two angles that are opposite each other when two lines intersect. Vertical angles are always congruent, meaning they have the same measure.
Clarifying Questions
What is the relationship between complementary angles?
Complementary angles are two angles that add up to 90 degrees.
How do you calculate the length of a segment formed by intersecting lines?
To calculate the length of a segment formed by intersecting lines, you can use the Pythagorean theorem.
What is the difference between congruent and parallel segments?
Congruent segments are segments that have the same length. Parallel segments are segments that lie in the same plane and never intersect.