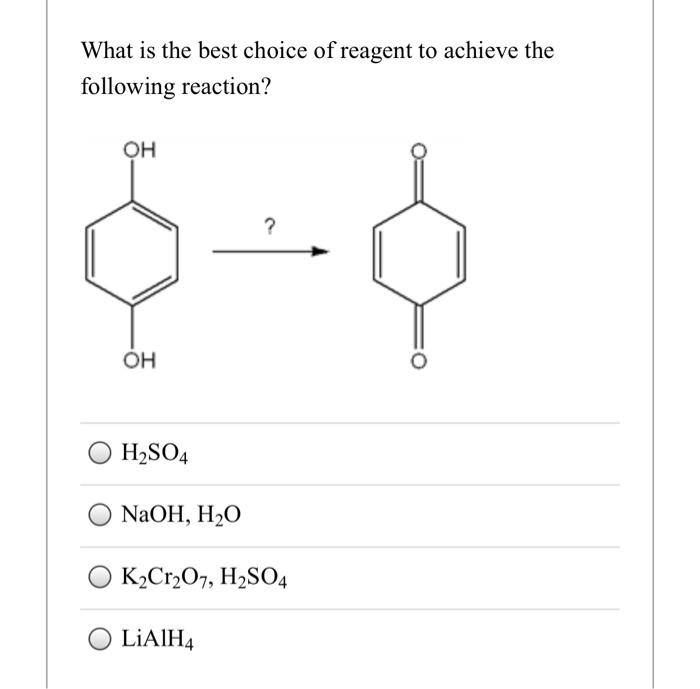
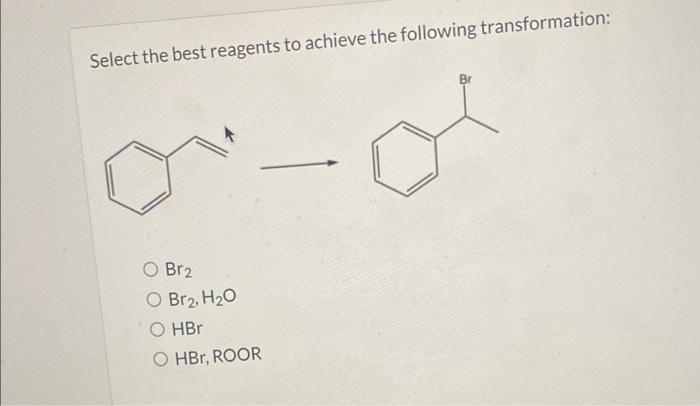
Select the best reagents to achieve the following transformation – Selecting the best reagents to achieve a desired chemical transformation is a crucial step in organic synthesis. It requires a deep understanding of reaction conditions, functional group interconversions, reagent selectivity, and regio- and stereoselectivity. This article delves into these concepts and provides guidelines for selecting the most effective reagents for specific transformations.
Factors such as temperature, pressure, solvent, and the nature of the functional groups involved influence reagent selection. The mechanisms of reactions and their impact on selectivity must also be considered. Additionally, green chemistry principles, cost, availability, and safety considerations play a significant role in the decision-making process.
Selecting the Best Reagents for Organic Synthesis
Selecting the appropriate reagents for organic synthesis is crucial to achieve desired reaction outcomes and optimize efficiency. Several factors influence reagent selection, including reaction conditions, functional group interconversions, reagent selectivity, regio- and stereoselectivity, green chemistry considerations, cost and availability, and safety.
Reaction Conditions
Reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and solvent, significantly impact reagent selection. Elevated temperatures can enhance reaction rates but may also lead to unwanted side reactions. Pressure can influence the equilibrium of reactions, and solvents can affect the solubility and reactivity of reagents.
Functional Group Interconversions
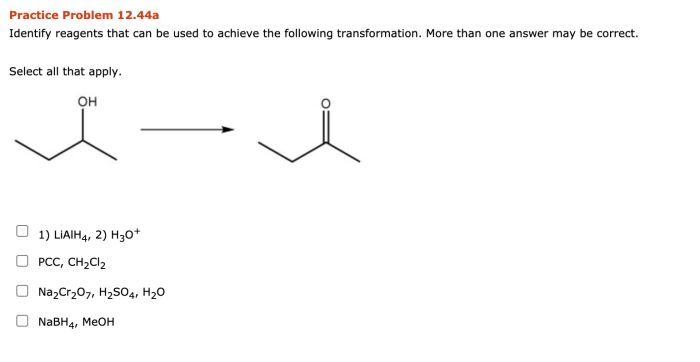
Functional group interconversions involve transforming one functional group into another. The choice of reagents depends on the specific functional groups involved and the desired outcome. For example, alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or ketones using oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate or chromic acid.
Reagent Selectivity
Reagent selectivity refers to the ability of a reagent to react with a specific functional group or position within a molecule. Steric hindrance and electronic effects influence reagent selectivity. Bulky reagents may be less selective due to steric hindrance, while electron-withdrawing groups can enhance the reactivity of certain functional groups.
Regio- and Stereoselectivity, Select the best reagents to achieve the following transformation
Regioselectivity and stereoselectivity are crucial in organic synthesis. Regioselectivity controls the position of the new bond formed, while stereoselectivity controls the spatial arrangement of atoms or groups around the new bond. Reagents can be selected to achieve specific regio- and stereochemical outcomes based on their mechanisms and substrate interactions.
Green Chemistry Considerations
Green chemistry principles promote the use of environmentally friendly reagents and reaction conditions. This involves selecting reagents with low toxicity, high biodegradability, and minimal waste generation. Solvent selection is also crucial, with a focus on non-toxic and renewable solvents.
Cost and Availability
Cost and availability of reagents are practical considerations in reagent selection. Expensive or scarce reagents may not be feasible for large-scale synthesis. Optimizing reagent selection based on cost and availability involves evaluating alternative reagents, considering bulk discounts, and exploring sustainable sourcing options.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount in reagent selection. Reagents should be handled and stored properly to minimize risks. Flammable, toxic, or corrosive reagents require special precautions and protective measures. Safety data sheets (SDSs) provide essential information on the hazards and handling guidelines for each reagent.
FAQ Section: Select The Best Reagents To Achieve The Following Transformation
What are the key factors to consider when selecting reagents?
Reaction conditions, functional group interconversions, reagent selectivity, regio- and stereoselectivity, green chemistry principles, cost, availability, and safety considerations are all important factors to consider.
How does regio- and stereoselectivity influence reagent selection?
Reagents can be selected to achieve specific regio- and stereochemical outcomes by considering their steric and electronic effects, as well as the reaction mechanisms involved.
What role does green chemistry play in reagent selection?
Green chemistry principles encourage the use of environmentally friendly reagents and reaction conditions, which can influence reagent selection.