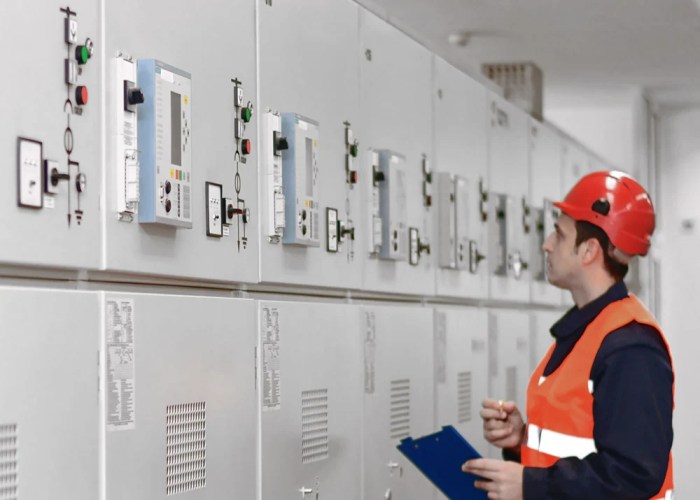
In the realm of electrical engineering, lesson 1 purpose of overcurrent protection and types of overcurrents delves into the crucial topic of safeguarding electrical systems from the damaging effects of excessive current. Overcurrent protection plays a pivotal role in ensuring the reliability and safety of electrical installations, and this introductory paragraph will provide an engaging overview of its purpose and the various types of overcurrents that can occur.
Electrical systems are designed to operate within specific current limits. When these limits are exceeded, overcurrents can arise, potentially leading to catastrophic consequences. Overcurrent protection devices, such as fuses and circuit breakers, are employed to detect and interrupt these excessive currents, preventing damage to equipment and minimizing the risk of electrical hazards.
Purpose of Overcurrent Protection

Overcurrent protection is a crucial aspect of electrical systems, safeguarding equipment and personnel from the detrimental effects of excessive current. It aims to prevent electrical fires, equipment damage, and other hazards that can arise when current exceeds the intended operating limits.
Overcurrent protection devices, such as fuses, circuit breakers, and relays, monitor the current flow and disconnect the circuit when it exceeds a predetermined threshold. These devices act as a safety barrier, preventing the damaging effects of overcurrents and ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electrical systems.
Types of Overcurrents
Overcurrents can be classified into various types, each with distinct causes and characteristics:
- Short-circuit currentsoccur when a low-resistance path is created between two conductors, causing a sudden and massive increase in current.
- Ground-fault currentsarise when a conductor comes into contact with the ground, creating a path for current to flow outside the intended circuit.
- Overload currentsoccur when the current exceeds the normal operating capacity of a circuit or equipment, typically due to excessive load demand or equipment malfunction.
- Arc-fault currentsresult from an electrical arc, which is a sustained electrical discharge between two conductors. Arc-faults can generate high levels of current and pose significant fire hazards.
Consequences of Overcurrents
Overcurrents can have severe consequences if not properly addressed. Excessive current can:
- Damage electrical equipmentby overheating and causing insulation breakdown.
- Start electrical firesby igniting combustible materials or creating sparks.
- Pose electrical hazardsto personnel, such as electric shock or arc flash.
Methods of Overcurrent Protection, Lesson 1 purpose of overcurrent protection and types of overcurrents
Overcurrent protection is achieved through various methods:
- Fusesare one-time devices that melt and break the circuit when current exceeds a specified level.
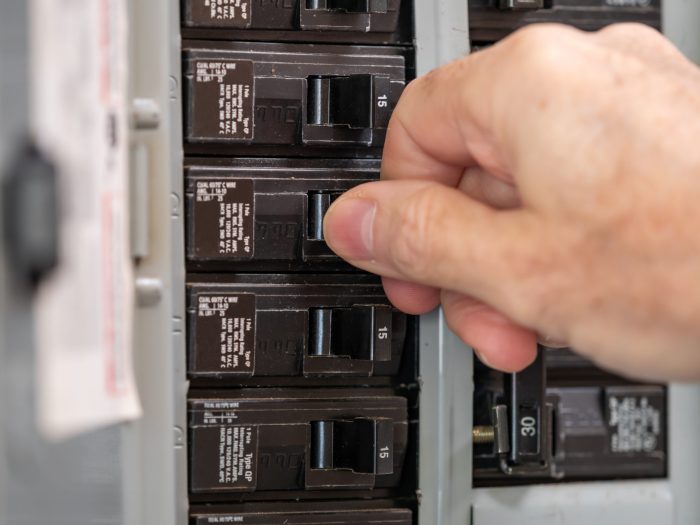
- Circuit breakersare reusable devices that automatically trip and open the circuit when current exceeds a threshold, and can be reset after the fault is cleared.
- Relaysare electronic devices that sense overcurrents and trigger the operation of circuit breakers or other protective devices.
- Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs)are specialized devices that detect ground-fault currents and quickly disconnect the circuit to prevent electric shock.
FAQ Compilation: Lesson 1 Purpose Of Overcurrent Protection And Types Of Overcurrents
What is the primary purpose of overcurrent protection?
Overcurrent protection aims to protect electrical equipment and systems from damage caused by excessive currents, preventing electrical hazards and ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
What are the different types of overcurrents?
Overcurrents can be classified into various types, including short-circuit currents, overload currents, ground fault currents, and arcing faults, each with its own unique characteristics and causes.
How can overcurrents be prevented?
Preventing overcurrents involves implementing proper electrical design practices, using appropriate wire sizes and circuit protection devices, and maintaining electrical equipment to minimize the risk of faults and excessive current flow.