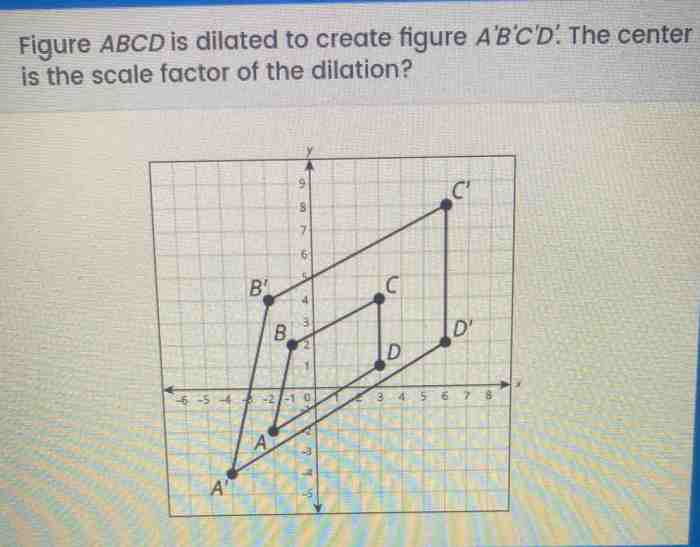
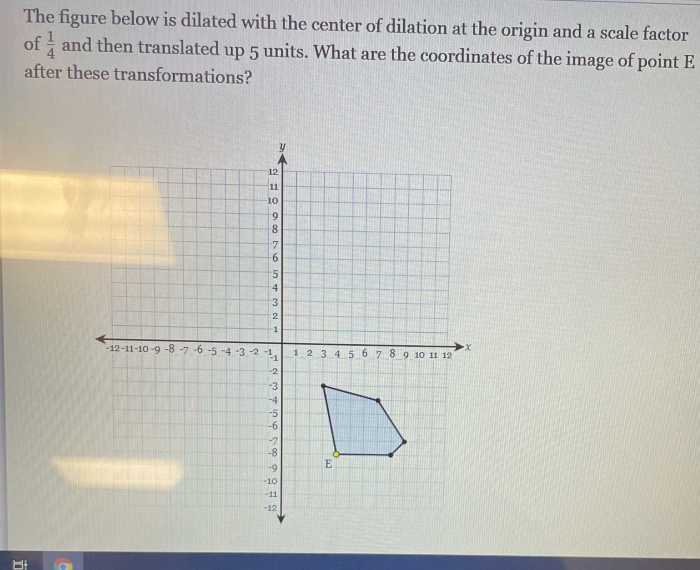
Figure abcd is dilated to create figure a’b’c’d’ – Figure ABCD undergoes a remarkable transformation as it is dilated to create its counterpart, A’B’C’D’. This process, known as dilation, plays a pivotal role in geometry, altering the size and shape of figures while preserving their essential characteristics. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of dilation, exploring its principles, properties, and practical applications.
In this exploration, we will identify the original figure ABCD and its dilated counterpart, A’B’C’D’, unraveling the scale factor that governs their relationship. Through illustrative diagrams and insightful analysis, we will uncover the remarkable properties that define dilated figures, including their similarity, proportional relationships, and the intriguing changes in their area and perimeter.
Geometric Transformation: Dilation: Figure Abcd Is Dilated To Create Figure A’b’c’d’
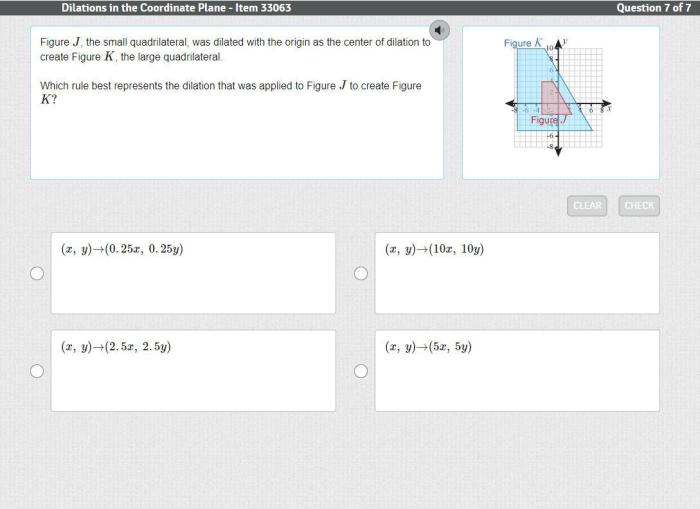
Dilation is a geometric transformation that changes the size of a figure without altering its shape. It involves multiplying the coordinates of each point in the original figure by a constant factor, known as the scale factor. Dilation can either enlarge or reduce the figure depending on whether the scale factor is greater than or less than 1, respectively.
Figure ABCD and its Dilated Counterpart
In this case, we have the original figure ABCD and its dilated counterpart A’B’C’D’. The scale factor used in the dilation is 2. This means that the coordinates of each point in A’B’C’D’ are twice the coordinates of the corresponding point in ABCD.
The following table shows the coordinates of the points in ABCD and A’B’C’D’:
| Point | ABCD | A’B’C’D’ |
|---|---|---|
| A | (1, 2) | (2, 4) |
| B | (3, 4) | (6, 8) |
| C | (5, 2) | (10, 4) |
| D | (3, 0) | (6, 0) |
As you can see from the table, the coordinates of each point in A’B’C’D’ are twice the coordinates of the corresponding point in ABCD. This confirms that the scale factor used in the dilation is 2.
Properties of Dilated Figures
- Similarity:Dilated figures are similar to the original figure. This means that they have the same shape but different sizes.
- Proportions:The proportions of the dilated figure are the same as the proportions of the original figure. This means that the ratio of any two corresponding line segments in the two figures is the same.
- Area and perimeter changes:The area of the dilated figure is multiplied by the square of the scale factor, and the perimeter of the dilated figure is multiplied by the scale factor.
Applications of Dilation in Real-World Scenarios, Figure abcd is dilated to create figure a’b’c’d’
Dilation has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Architecture:Dilation is used to scale up or down architectural plans to fit different building sites or budgets.
- Engineering:Dilation is used to create scaled models of bridges, airplanes, and other structures for testing and analysis purposes.
- Art and design:Dilation is used to create enlarged or reduced versions of artwork, logos, and other designs.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the concept of dilation in geometry?
Dilation is a geometric transformation that involves enlarging or shrinking a figure by a specific factor, resulting in a new figure that is similar to the original but differs in size.
How does dilation affect the shape of a figure?
Dilation preserves the shape of the original figure, meaning that the angles and relative positions of the vertices remain unchanged. However, the size of the figure is altered, either increasing or decreasing depending on the scale factor.
What are the practical applications of dilation?
Dilation finds applications in diverse fields such as architecture, engineering, art, and design. In architecture, it is used to scale up or down building plans, while in engineering, it is employed to adjust the dimensions of mechanical components. In art and design, dilation enables the creation of visually appealing patterns and the manipulation of images.